Android DHCP 9: The Hidden Gem You Need to See
Android devices, from smartphones to tablets, are ubiquitous in our daily lives. We rely on them for communication, entertainment, and productivity. But have you ever stopped to consider how your device connects to the internet, especially on a local network? Behind the scenes, a crucial protocol called DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) works tirelessly. And within the Android ecosystem, specifically, delving into DHCP configuration can unlock a hidden layer of network management and troubleshooting. This article will explore Android DHCP 9, offering insights into its functionality and why it’s a valuable tool for both tech enthusiasts and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of their network connections.
Understanding DHCP: The Foundation of Network Connectivity
Before we dive into Android DHCP 9, let’s establish the basics. DHCP is a network management protocol used on IP networks whereby a DHCP server dynamically assigns an IP address and other network configuration parameters to each device on the network so they can communicate with other IP networks. Think of it like a hotel concierge for your device:
- Assigning IP Addresses: DHCP automatically provides devices with unique IP addresses, allowing them to communicate on the network.
- Providing Gateway Information: It tells your device where to find the gateway (usually your router), the pathway to the internet.
- Specifying DNS Servers: DHCP also provides the addresses of DNS (Domain Name System) servers, which translate website names into IP addresses.
- Automatic Configuration: DHCP eliminates the need for manual IP address configuration, saving time and reducing the potential for errors.
Without DHCP, setting up and maintaining a network would be a significantly more complex and time-consuming process.
Android DHCP 9: Unveiling the Details
While the specifics of Android DHCP configurations are often hidden beneath the user interface, version 9 (and its subsequent iterations) of the Android operating system brought about refinements and improvements. It’s crucial to realize that the exact behaviour and options available can vary based on the Android device manufacturer, the Android version, and the underlying network infrastructure.
Here’s what you might encounter when interacting with Android DHCP (though direct user interaction is often limited):
- Automatic IP Address Assignment: By default, Android devices are configured to obtain an IP address automatically from the DHCP server on the network.
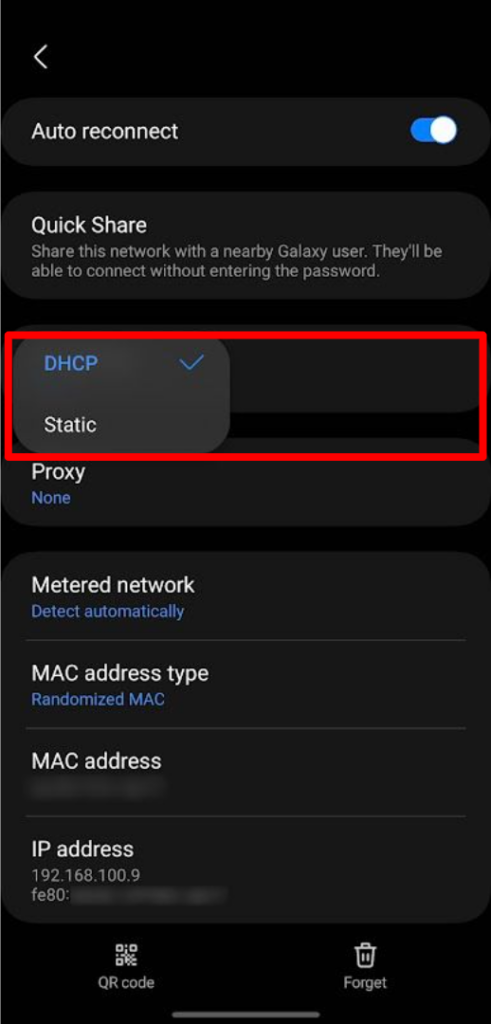
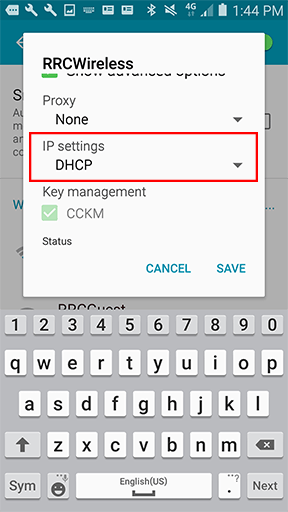
- Static IP Configuration (Limited): While direct manual configuration is frequently restricted in the user interface, some device manufacturers might allow users to configure a static IP address. In this case, you would manually input the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS servers.
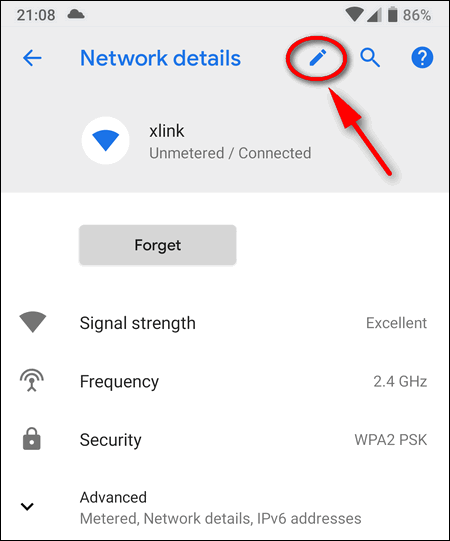
- Network Information Display: You can typically view the IP address, gateway, DNS servers, and other network details assigned by DHCP within the device’s network settings. (Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi, then tap on the connected network, and check the details.)
- Troubleshooting Tools: Android includes built-in network diagnostics that can help identify DHCP-related issues, such as a failure to obtain an IP address.
Troubleshooting Common DHCP Problems on Android
Sometimes, your Android device might encounter issues connecting to the network. Here are some common problems and potential solutions:
- Failing to Obtain an IP Address:
- Problem: Your device doesn’t get an IP address from the DHCP server.
- Solutions:
- Restart your device and the router.
- Check the router’s DHCP server settings to ensure it’s enabled and has available IP addresses.
- Try forgetting and rejoining the Wi-Fi network on your Android device.
- Slow Internet Speed:
- Problem: Your internet connection is slow, even though the Wi-Fi signal strength is good.
- Solutions:
- Check the DNS server settings. You may need to switch to a different DNS server (like Google’s public DNS: 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4, or Cloudflare’s DNS: 1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1).
- Check your router’s internet connection speed and make sure it matches your subscribed plan.
- Intermittent Connectivity:
- Problem: Your device loses connection frequently.
- Solutions:
- Ensure your router’s firmware is up to date.
- Check for interference from other devices or networks.
- Try resetting your router to factory defaults (after backing up your settings).
Android DHCP 9 and Beyond: The Future of Network Connectivity
Android continues to evolve, and so does its handling of network configurations. Each new release often brings improvements to DHCP management, security enhancements, and support for the latest network technologies. While direct user interaction with DHCP settings is usually limited, understanding the underlying principles remains valuable for effective troubleshooting and network awareness.
FAQs about Android DHCP
How do I find my Android device’s IP address? Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi, then tap on the connected network. Your IP address, gateway, and DNS servers will be displayed in the details section.
Can I manually set a static IP address on my Android device? While this is often locked down, some manufacturers may provide the option. Within the Wi-Fi settings, tap on the connected network, and look for “Advanced Options” or a similar setting. If available, you can change the IP settings from DHCP to Static.
What is the difference between DHCP and a static IP address? DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses, while a static IP address is manually configured and remains constant. DHCP is generally easier to manage, especially on larger networks. Static IPs are useful for devices that need a consistent IP address (e.g., network printers or servers).
Why is my Android device not connecting to the Wi-Fi network? There could be several reasons: incorrect Wi-Fi password, the router isn’t broadcasting the SSID, or a DHCP issue. Ensure the password is correct, restart your router, and check the router’s configuration.
Is it safe to use public Wi-Fi networks? Public Wi-Fi networks can be less secure. Avoid transmitting sensitive information (banking, personal data) on public networks. Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to encrypt your internet traffic for enhanced security.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Understanding
Android DHCP 9, and its subsequent iterations, may be a hidden aspect of your device’s functionality, but it plays a vital role in how you connect to the internet. By understanding the basics of DHCP and how it functions on Android devices, you can troubleshoot network problems more effectively, optimize your connection, and gain a deeper appreciation for the technology that powers your digital life. While direct interaction with DHCP settings is usually limited, the knowledge empowers you to be a more informed and capable user.