From Forehead to Chin: A Comprehensive Guide to the Parts of the Head and Face
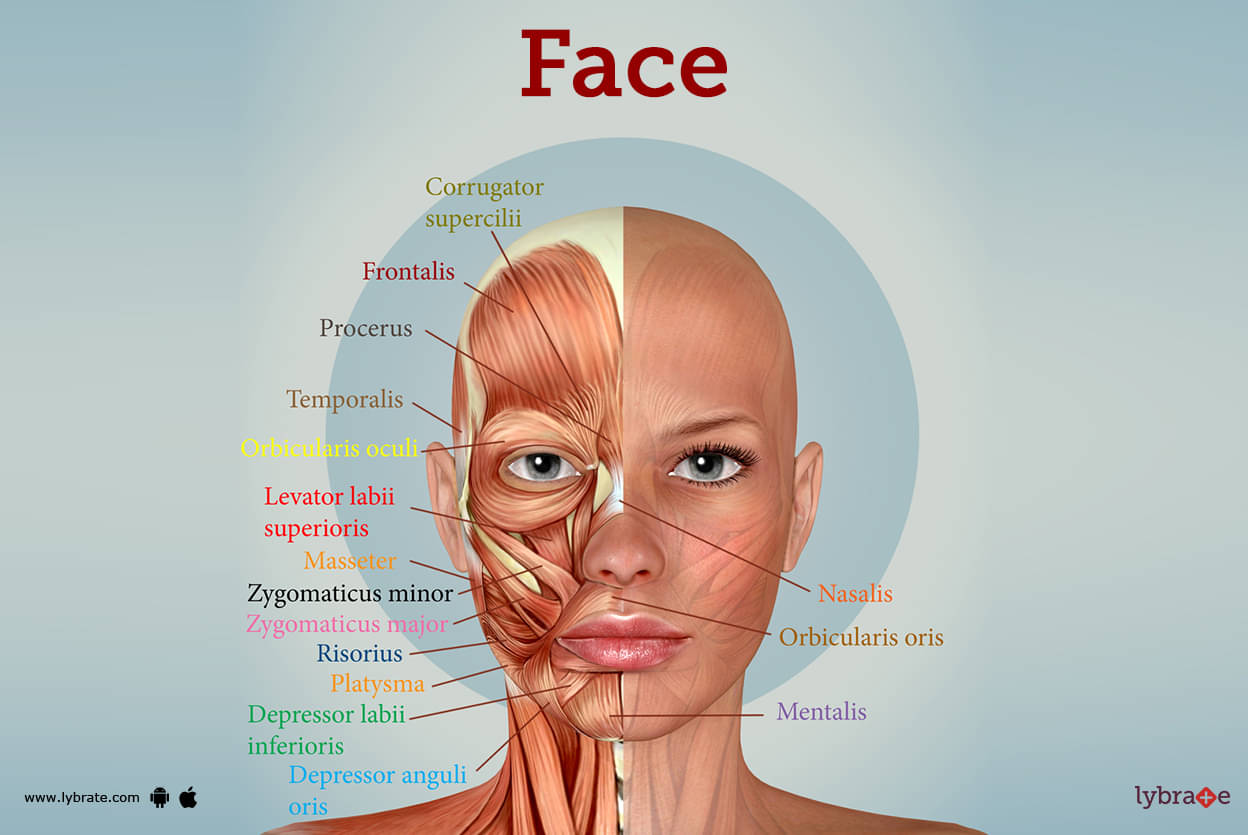
The human face is a marvel of biological engineering. A canvas for expression, a gateway for senses, and a key identifier for individuals, it’s a complex and fascinating area. Understanding the anatomy of the head and face is crucial for various fields, from medicine and cosmetology to art and communication. This comprehensive guide will take you on a journey, from the highest point of your forehead to the tip of your chin, naming every part of this intricate landscape.
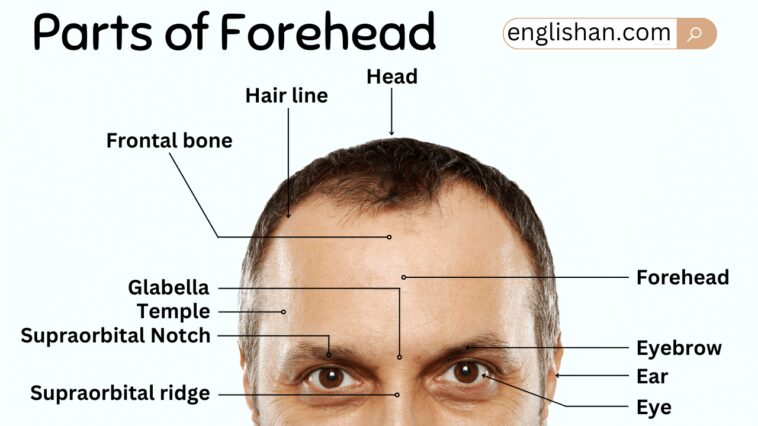
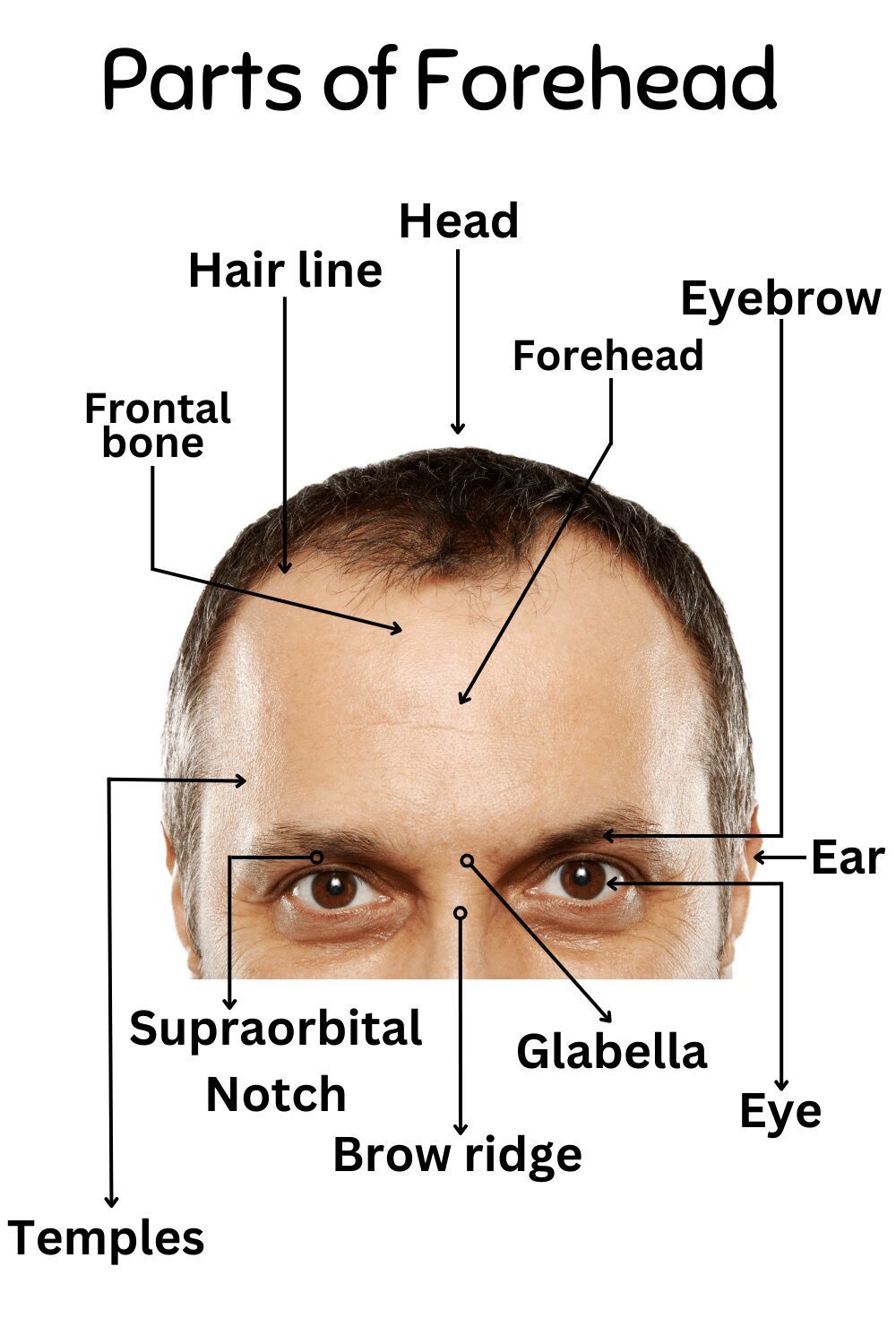
The Forehead: The Cranial Canvas
The forehead, or frontal region, forms the upper portion of the face. It’s primarily comprised of the frontal bone, which protects the brain.
- Key Features:
- Frontal Bone: The main bone forming the forehead.
- Hairline: The edge of the scalp where hair growth begins.
- Eyebrows: Arched ridges of hair above the eyes, protecting them from sweat and sunlight.
- Glabella: The smooth area between the eyebrows, above the nose.
- Supraorbital Ridges: The bony ridges beneath the eyebrows.
The Eyes: Windows to the Soul
The eyes, or the orbital region, are responsible for sight, and are complex structures protected by several layers.
- Key Features:
- Eyelids: Folds of skin that protect the eye and regulate light.
- Eyelashes: Hairs that protect the eye from debris.
- Eyeball (Globe): The spherical organ responsible for vision.
- Pupil: The dark, central opening that allows light to enter the eye.
- Iris: The colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil.
- Sclera: The white outer layer of the eyeball.
- Canthus (Inner and Outer): The corners of the eye.
- Lacrimal Caruncle: A small, reddish nodule in the inner corner of the eye.
The Nose: The Olfactory and Respiratory Gateway
The nose, or nasal region, serves as the primary organ for smell and a critical part of the respiratory system.
- Key Features:
- Bridge: The bony upper part of the nose.
- Nasal Root: The area where the nose begins between the eyes.
- Nasal Dorsum (Ridge): The upper, prominent part of the nose.
- Nares (Nostrils): The external openings of the nose.
- Nasal Tip: The rounded end of the nose.
- Alae (Wings): The flared sides of the nostrils.
The Cheeks: The Facial Bulwark
The cheeks, or buccal region, form the sides of the face and are primarily composed of soft tissue and the underlying bones of the maxilla and zygomatic arch.
- Key Features:
- Cheekbones (Zygomatic Bones): The prominent bones forming the upper part of the cheeks.
- Cheek: The fleshy part of the face below the eyes and between the nose and ears.
- Philtrum: The vertical groove between the nose and the upper lip.
The Ears: Organs of Hearing and Balance
The ears, or auricular region, are responsible for hearing and maintaining balance. They are located on either side of the head.
- Key Features:
- Pinna (Auricle): The visible outer part of the ear.
- Helix: The outer rim of the ear.
- Antihelix: The inner, curved ridge parallel to the helix.
- Tragus: The small flap of cartilage in front of the ear canal.
- Antitragus: The small flap of cartilage opposite the tragus.
- Lobe: The fleshy lower part of the ear.
- Ear Canal (External Auditory Meatus): The opening leading to the inner ear.
The Mouth and Lips: The Gateway to Speech and Nourishment
The mouth and lips, or oral region, are essential for speech, eating, and expression.
- Key Features:
- Lips (Labia): The fleshy borders of the mouth.
- Upper Lip: The lip above the mouth.
- Lower Lip: The lip below the mouth.
- Vermilion Border: The red border of the lips.
- Philtrum: The vertical groove above the upper lip.
- Oral Cavity (Mouth): The space within the lips containing the teeth and tongue.
- Chin: The lower part of the face, forming the end of the jawline.
- Gums: The fleshy tissues surrounding the teeth.
- Teeth: The hard, bony structures used for chewing.
- Tongue: The muscular organ within the mouth used for taste, speech, and swallowing.
The Chin: The Final Frontier
The chin, or mental region, forms the bottommost part of the face. It’s a bony prominence that completes the facial structure.
- Key Features:
- Mental Protuberance: The bony prominence of the chin.
- Chin Cleft: The vertical indentation sometimes present on the chin.
Conclusion: A Symphony of Structures
From the forehead to the chin, the human face is a complex and interconnected system. Understanding the names and locations of the different parts of the head and face is crucial for various disciplines. This guide provides a foundational understanding of facial anatomy, empowering you with the knowledge to appreciate the intricate beauty and functionality of this vital area.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the function of the philtrum?
The philtrum, the vertical groove between the nose and the upper lip, is a remnant of how the face develops in the womb. It doesn’t have a specific, vital function, but it adds to the unique features of the face.
2. What are the different layers of the skin on the face?
The skin on the face, like skin everywhere else on the body, has three main layers: the epidermis (outer layer), the dermis (middle layer containing blood vessels and nerves), and the subcutaneous layer (innermost layer containing fat and connective tissue).
3. What is the purpose of the eyebrows?
Eyebrows serve several important functions. They help to protect the eyes from sweat, rain, and sunlight. They also play a significant role in facial expression, contributing to communication and social interaction.
4. Where is the zygomatic arch located?
The zygomatic arch, often referred to as the cheekbone, is located on the side of the face, forming the prominent ridge below the eye and extending towards the ear. It is formed by the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) and the temporal bone.
5. What is the vermilion border?
The vermilion border is the reddish outline of the lips. It is the transitional zone between the skin of the face and the mucous membrane of the lips.