Mixing Pain Relievers: Understanding Tylenol, Excedrin Migraine, and Safe Practices
Headaches are a common ailment, and when pain strikes, the search for relief begins. Many people reach for over-the-counter pain relievers like Tylenol (acetaminophen) and Excedrin Migraine. But what happens when one medication isn’t enough? Can you safely mix Tylenol and Excedrin Migraine? This article provides a comprehensive overview of these medications, potential risks, and how to navigate pain relief safely.
Understanding the Medications: Tylenol and Excedrin Migraine
Before considering mixing medications, it’s crucial to understand their individual components and how they work.
Tylenol (Acetaminophen):
- Mechanism: Primarily works by reducing pain signals in the brain and spinal cord. It also helps to lower fever.
- Uses: Effective for mild to moderate pain, including headaches, muscle aches, and fever.
- Important Note: Acetaminophen is processed by the liver. Excessive doses can lead to liver damage.
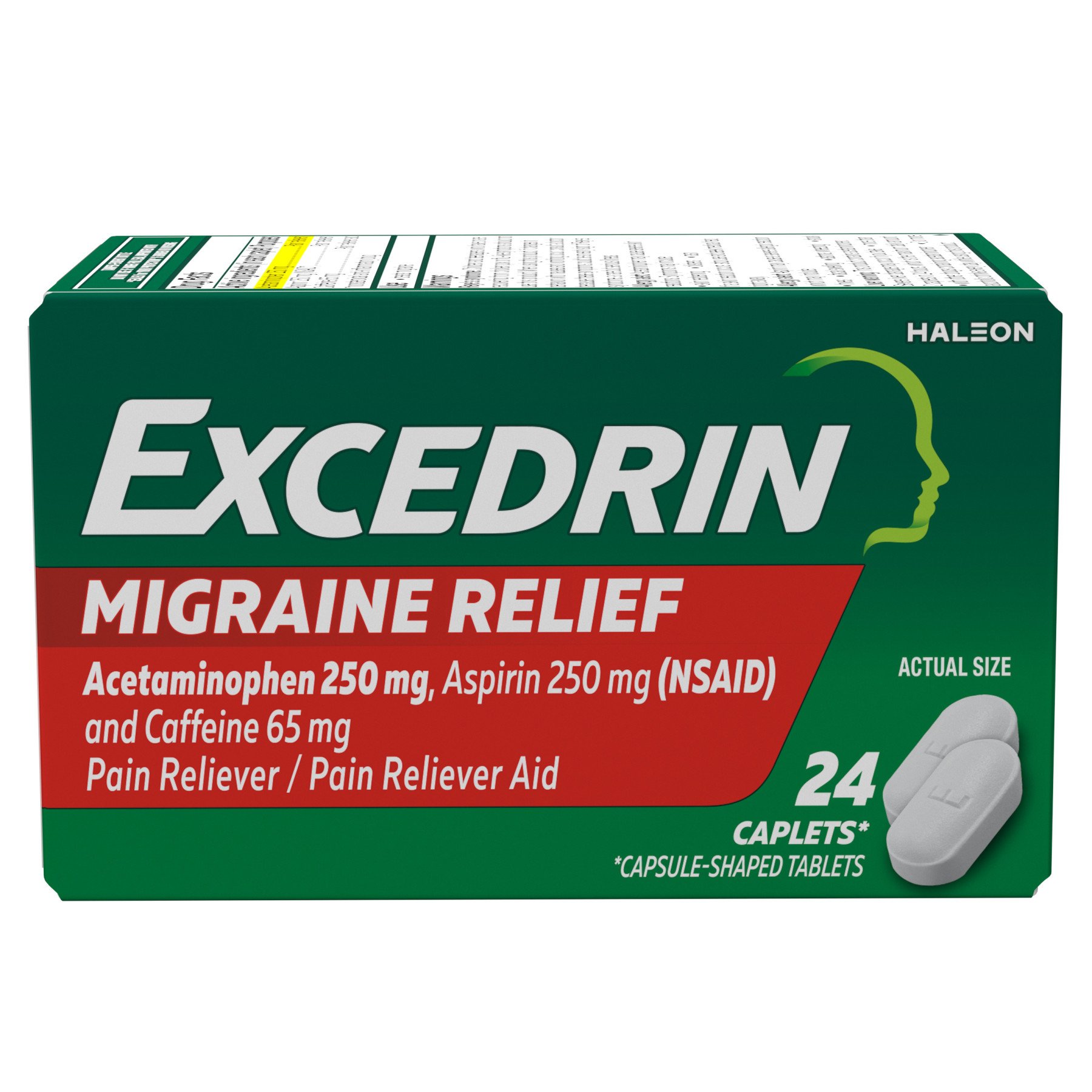
Excedrin Migraine:
- Components: Excedrin Migraine combines three active ingredients:
- Acetaminophen (250 mg): The same pain reliever found in Tylenol.
- Aspirin (250 mg): A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that reduces pain, inflammation, and fever.
- Caffeine (65 mg): A stimulant that can help constrict blood vessels in the brain, potentially alleviating headache pain and enhancing the effects of the other ingredients.
- Uses: Specifically formulated for migraine headaches, offering a combination of pain relief and potential vasoconstriction.
- Important Note: Aspirin can thin the blood and should be avoided or used with caution by people with bleeding disorders or taking blood thinners. Caffeine can contribute to anxiety, insomnia, and other side effects.
Can You Take Tylenol and Excedrin Migraine Together?
Generally, it is not recommended to take Tylenol and Excedrin Migraine simultaneously. This is because both medications contain acetaminophen.
- Risk of Overdose: Taking both together significantly increases your risk of exceeding the maximum daily dose of acetaminophen, which is 4,000 milligrams for healthy adults.
- Liver Damage: Overdosing on acetaminophen can lead to severe liver damage, potentially requiring a liver transplant or leading to death.
Important Considerations:
- Read Labels Carefully: Always check the active ingredients in all medications you are taking, including those for colds, coughs, and other ailments. Many over-the-counter products contain acetaminophen.
- Consult Your Doctor or Pharmacist: If your pain is not adequately controlled by Excedrin Migraine, or if you’re unsure about the safety of combining any medications, consult a healthcare professional. They can assess your specific situation, consider your medical history, and provide personalized advice.
- Staggering Doses (with Caution and Doctor Approval): In rare cases, a doctor might advise staggering doses of acetaminophen-containing medications. However, this is highly individualized and requires close monitoring. It is never a safe approach without professional guidance.
Safe Practices for Pain Management
Here’s how to approach pain management safely and effectively:
- Start with the Lowest Effective Dose: Always begin with the lowest recommended dose of a pain reliever.
- Follow Dosage Instructions: Adhere strictly to the dosage instructions on the product label. Do not exceed the recommended dose or frequency.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can increase the risk of liver damage when taking acetaminophen.
- Consider Alternative Therapies: Explore non-pharmacological approaches to pain management, such as:
- Rest and relaxation techniques
- Applying a cold compress
- Staying hydrated
- Identifying and avoiding headache triggers
- Seek Medical Attention: Consult a doctor if your headaches are severe, frequent, or accompanied by other symptoms (e.g., fever, stiff neck, vision changes, numbness).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some common questions about mixing Tylenol and Excedrin Migraine:
1. Is it safe to take Tylenol after taking Excedrin Migraine?
No, it’s generally not safe. Both medications contain acetaminophen. You should wait until the effects of Excedrin Migraine have worn off before taking any other medication containing acetaminophen. Consult your doctor about the appropriate time frame.
2. What happens if I accidentally take too much acetaminophen?
Overdosing on acetaminophen can cause liver damage. Symptoms of an overdose can include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice). Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect an overdose.
3. Can I take Excedrin Migraine for other types of headaches?
Excedrin Migraine is specifically formulated for migraine headaches. It may be effective for other types of headaches, but it’s best to consult a doctor or pharmacist to ensure it’s the right choice for your specific headache type.
4. What are the side effects of Excedrin Migraine?
Common side effects can include nausea, vomiting, stomach upset, nervousness, and insomnia. Aspirin can cause stomach irritation and, in some cases, increase the risk of bleeding. Caffeine can contribute to anxiety and sleep disturbances.
5. When should I see a doctor for my headaches?
You should consult a doctor if your headaches are severe, persistent, or if you experience any of the following symptoms: sudden onset of a severe headache, fever, stiff neck, vision changes, weakness, numbness, or confusion.
Conclusion
Managing pain effectively and safely requires understanding the medications you’re taking and adhering to recommended guidelines. While Tylenol and Excedrin Migraine can provide relief, mixing them is generally unsafe due to the risk of acetaminophen overdose. Always prioritize your health by reading labels carefully, following dosage instructions, and consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance. Remember, proper pain management is a collaborative effort between you and your doctor.